There is an urgent need to bridge the gap between national development agendas and the harsh realities experienced by marginalised tribal communities
In recent years, India has made significant strides in various sectors, ranging from space exploration to technological advancements. However, amidst this progress, the indigenous tribal communities of the country continue to grapple with numerous challenges that hinder their development and well-being. This article delves into the multifaceted issues faced by tribal populations in India, highlighting the urgent need for concerted efforts to address their needs and bridge the existing socio-economic gaps.
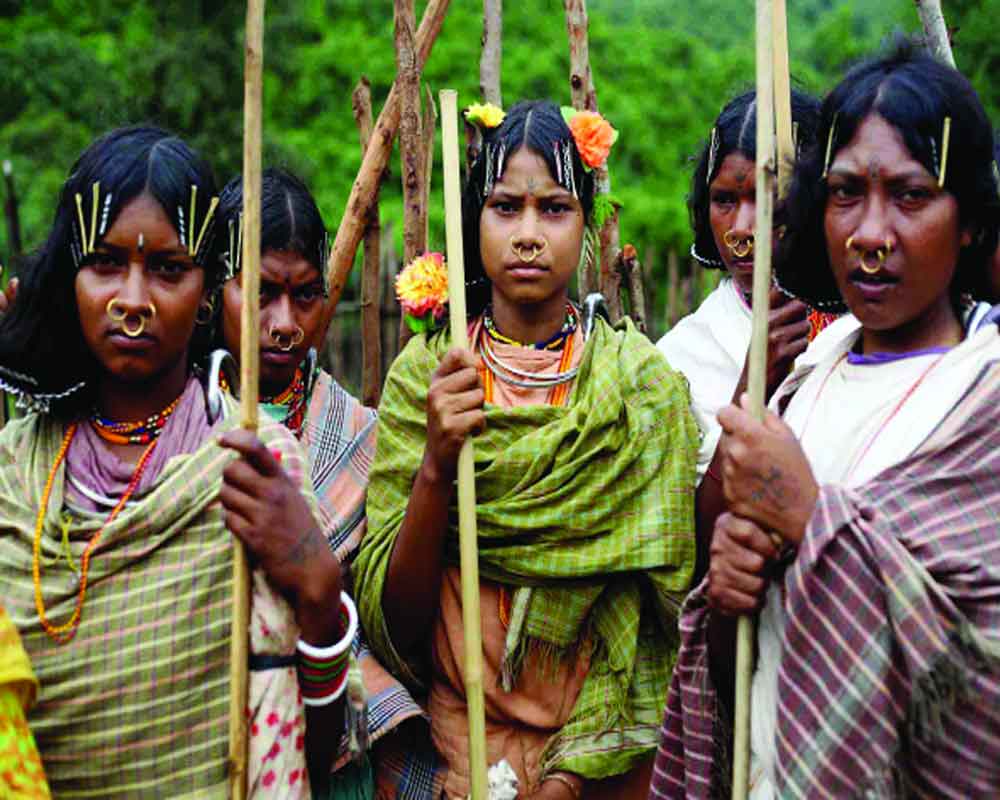
Tribal communities, often referred to as Adivasis, constitute a significant portion of India’s population, with approximately 10 crore individuals spread across various states. Despite their diverse cultures, languages, and traditions, these communities share common experiences of marginalisation and socio-economic disparities. Historically, they maintain a symbiotic relationship with nature and relying on traditional livelihood practices such as agriculture, hunting, and gathering.
Challenges faced: Despite efforts to improve access to education, tribal communities continue to face challenges in achieving educational parity. The literacy rate among tribal populations stands at a concerning 59 per cent, significantly lower than the national average. Factors such as inadequate infrastructure, teacher shortages, and cultural barriers contribute to this educational deficit, perpetuating cycles of poverty .
Tribal communities experience disproportionately high rates of malnutrition, with 39.5 per cent of individuals suffering from nutritional deficiencies, according to the National Family Health Survey. Additionally, diseases such as Sickle Cell Disease (SCD) and thalassemia are prevalent among tribal populations, highlighting the inadequate healthcare infrastructure and access to medical facilities in tribal areas.
Land rights issues are a longstanding concern for tribal communities, with many facing displacement due to development projects, natural calamities, and encroachment by mainstream society. Violations of constitutional safeguards meant to protect tribal lands, such as the Panchayats (Extension to Scheduled Areas) Act (PESA), further exacerbate their vulnerability.
Limited access to markets, credit facilities, and technology impedes the economic development of tribal communities, perpetuating cycles of poverty and dependency. Despite possessing valuable skills in areas such as agriculture, handicrafts, and traditional medicine, tribal artisans often struggle to access markets and receive fair compensation for their products.
Tribal communities frequently face discrimination and exploitation, both within their communities and in interactions with mainstream society. Issues such as human trafficking, wrongful incarceration, and forced displacement underscore the vulnerability of tribal populations and the urgent need for legal protections and social support mechanisms.
Initiatives and Interventions:
Efforts to improve access to quality education and vocational training programmes can enhance the employability and socio-economic status of tribal youth. Initiatives such as residential schools, scholarships, and skill development schemes play a crucial role in bridging the education gap and equipping tribal communities with the necessary skills for sustainable livelihoods.
Investments in healthcare infrastructure, mobile medical units, and community health workers can improve access to essential healthcare services in remote tribal areas. Awareness campaigns, preventive healthcare initiatives, and capacity-building programmes for healthcare professionals are essential for addressing the prevalent health challenges among tribal populations.
Strengthening legal protections for tribal land rights, ensuring participatory decision-making processes, and promoting sustainable natural resource management practices are critical for safeguarding the livelihoods and cultural heritage of tribal communities. Land titling initiatives, community forest rights, and alternative livelihood options can empower tribal communities to assert their rights and achieve economic self-reliance.
Supporting tribal entrepreneurship and facilitating market linkages can unlock the economic potential of tribal communities. Initiatives such as tribal cooperatives, marketing networks, and entrepreneurship development programmes enable tribal artisans and farmers to access markets and achieve fair prices for their products.
Social Inclusion: Promoting social cohesion, cultural diversity, and gender equality within tribal communities are essential for addressing social discrimination and exploitation. Community organisations, self-help groups, and advocacy efforts play a vital role in amplifying the voices of tribal communities and advocating for their rights and dignity.
Case Studies: The ITDA model, implemented in tribal-dominated regions of Andhra Pradesh, focuses on holistic development interventions, including education, healthcare, infrastructure, and livelihood promotion. Through targeted interventions such as skill development programmes, healthcare camps, and infrastructure projects, ITDAs have made significant strides in improving the well-being and livelihoods of tribal communities.
The Tribal Entrepreneurship Development Programme in Odisha aims to promote entrepreneurship among tribal youth by providing training, mentoring, and financial support for business startups. Through initiatives such as entrepreneurship awareness camps, skill development workshops, and access to credit facilities, the programme has empowered tribal entrepreneurs to launch successful businesses and contribute to local economic development.
(The writer is Vice-Chancellor at Central Tribal University of Andhra Pradesh; views are personal)